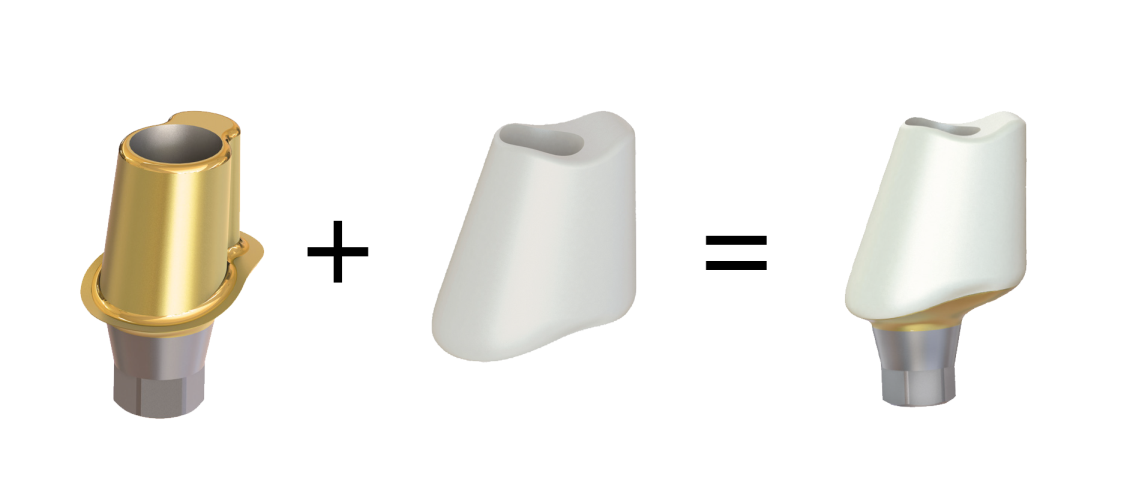We from Abutments4life
® would like to place all information about the application of the angulated titanium implant base here. Our aim is to facilitate the best possible esthetics and long-term stability at significantly reduced costs.
Welcome to Abutment solution with LTS-BASE
®.
Development of Abutments
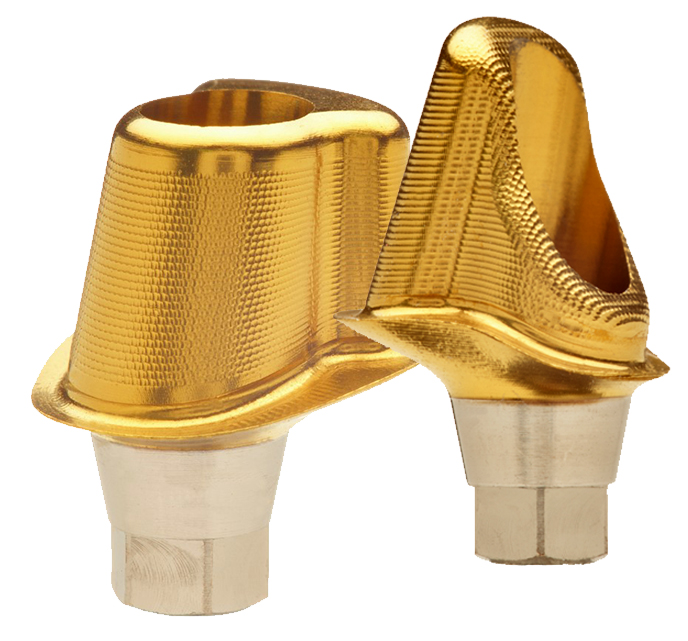
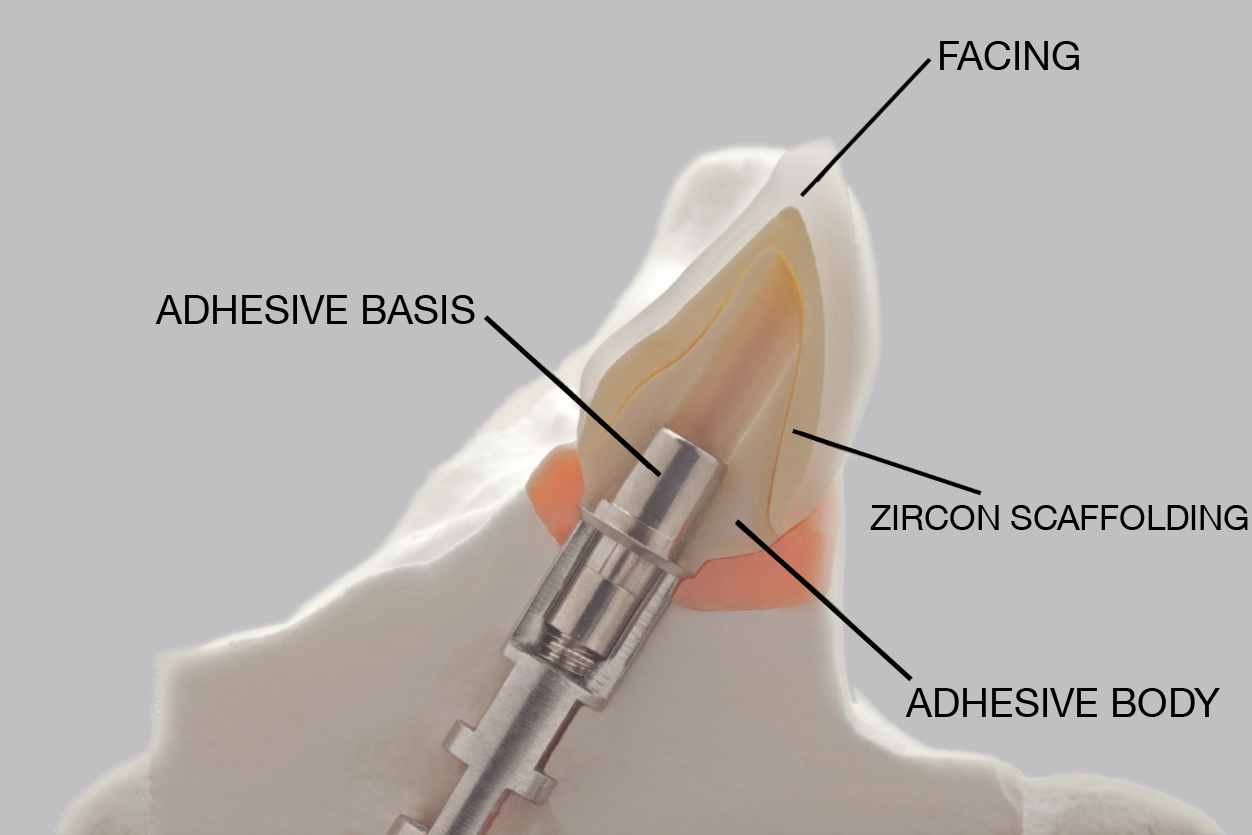
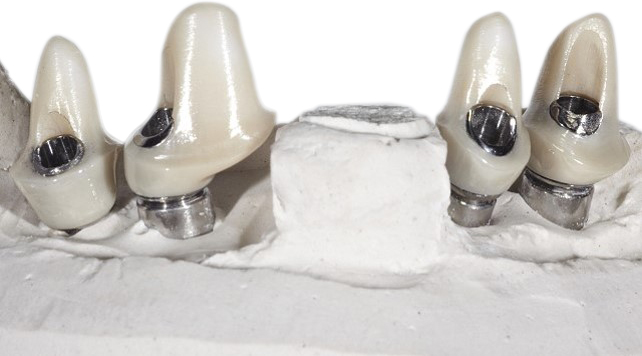
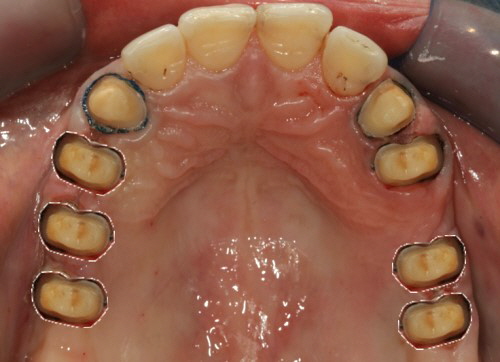
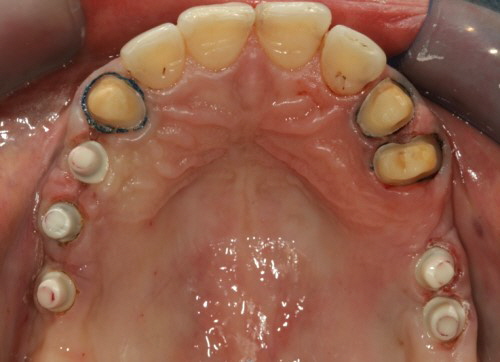
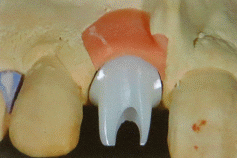
All hitherto full-titanium abutments were and are still used successfully when fixing a crown onto an implant. They are straight and available with different angulations and in most cases they consist of titanium grade 5. But they are increasingly being replaced by hybrid abutments having a titanium base and a ceramic body.
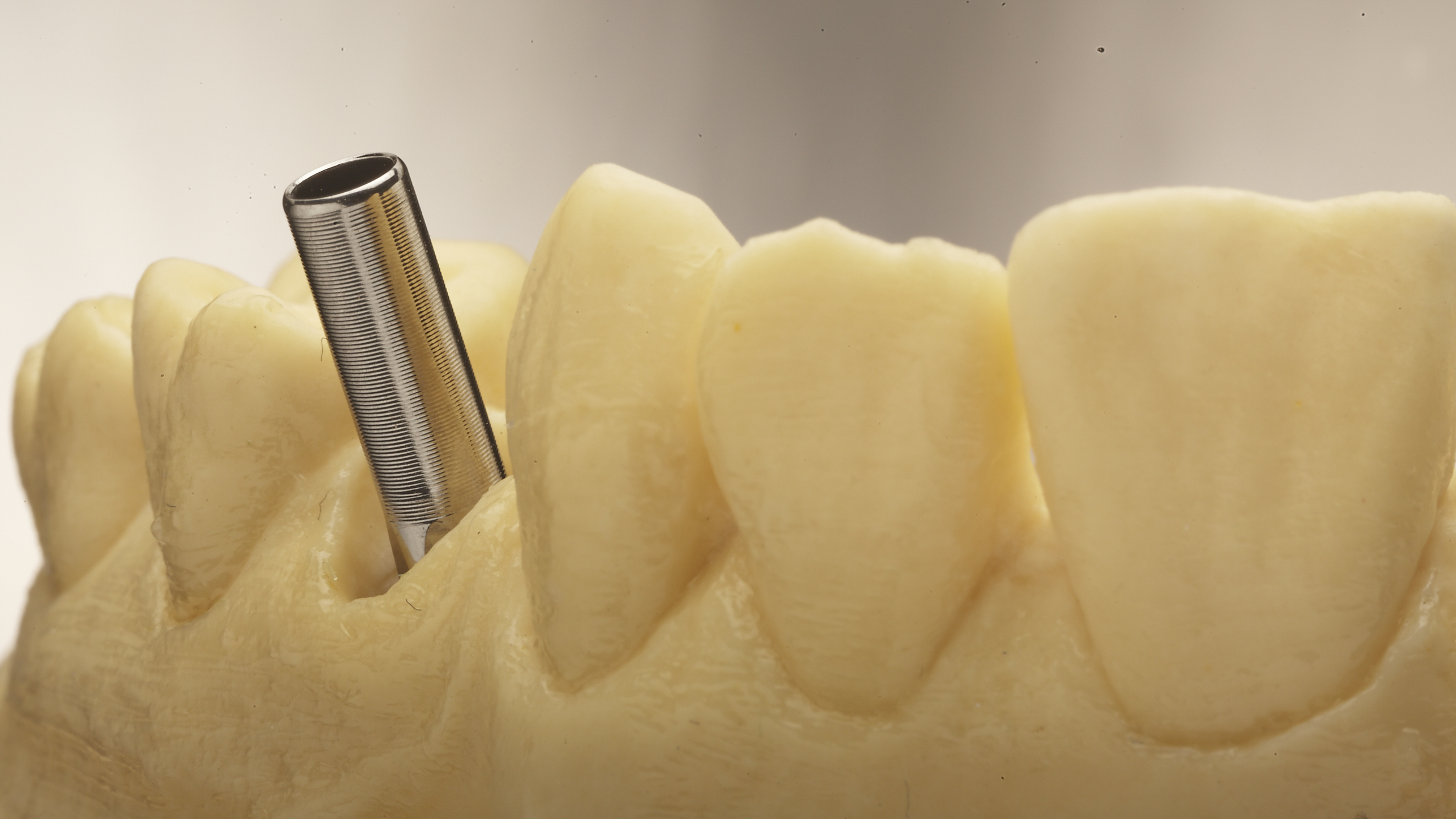
Previous adhesive bases for hybrid abutments were only available in straight form, i.e. having the screw channel in the prolongation of the implant axis. The new LTS-BASE® offers, for the first time, an adhesive basis for hybrid abutments having an angulated screw channel.
Angulated abutments
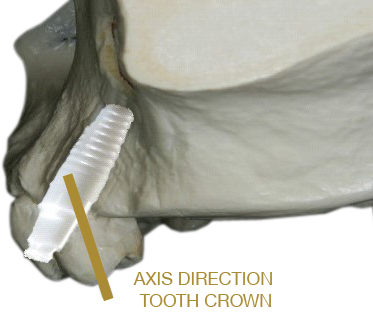
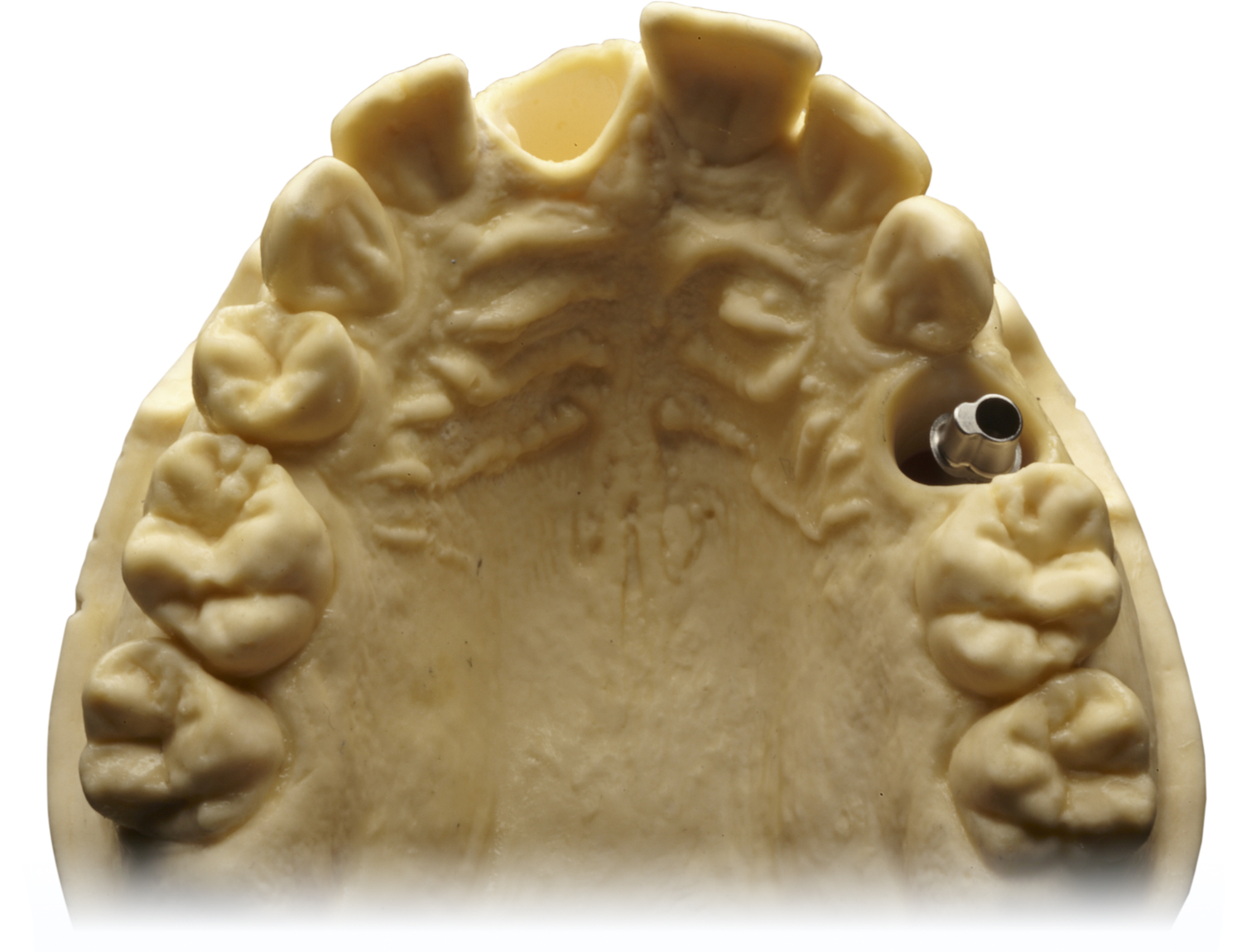
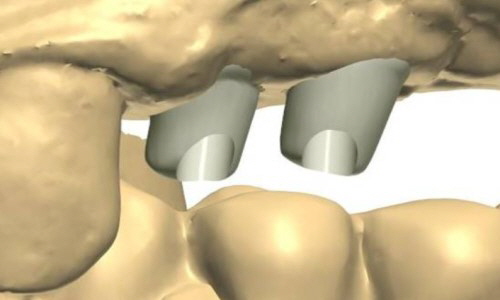
The anatomy of the bone determines the direction of the axis for the implant, with the screw head restricting the maximum possible angulation.
In transversal and sagittal direction an adverse implant position may occur.
CAD vs. Clinics
There is very often a big difference between CAD design and the clinical situation.
This problem may be solved in various ways with titanium abutments:
A) The preparation margin is extremely far and unpredictably placed underneath the gingiva. But there is a big danger of cement leftovers remaining there after cementing.
B) The wrongly placed preparation margin has again to be moulded to adapt the abutment in the laboratory.
This procedure takes more time and is more expensive. Titanium abutments cannot be grounded intra-orally because of the danger of some tattooings.
Being screwed vs. being cemented
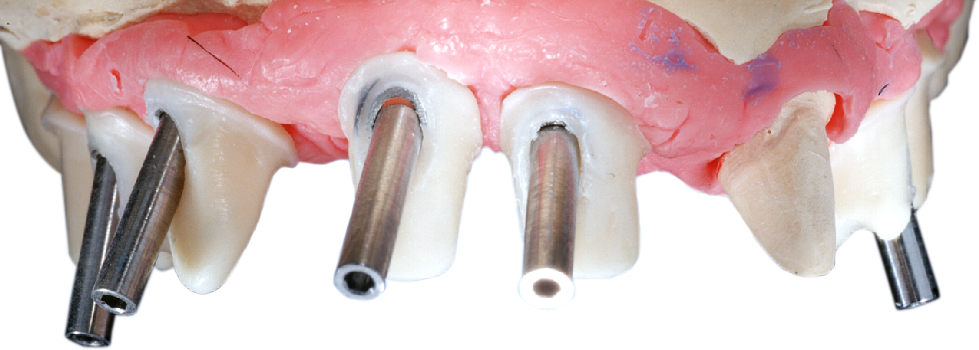
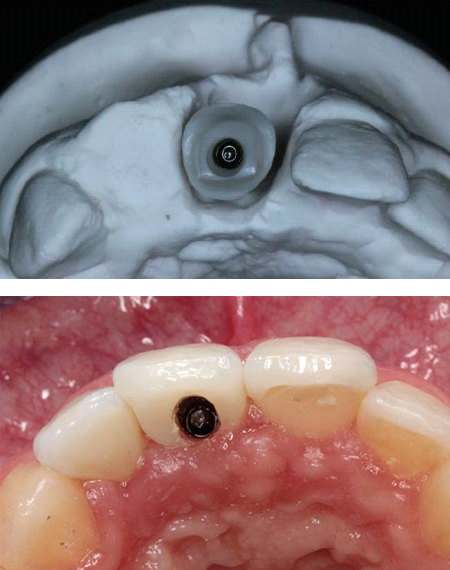
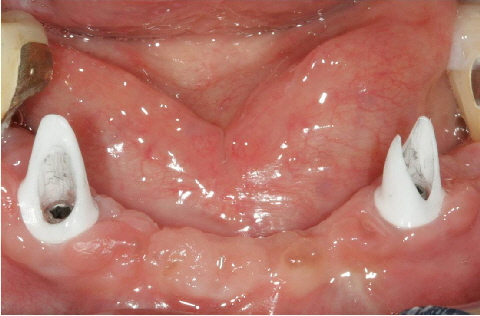
If an angulation of the crown will be necessary, clinical situations may receive a prosthetic restoration when using the angulated screw access channel of the LTS-BASE®.
According to clinical studies, this holds true in more than 80 per cent of the cases in the aesthetic visual range.
Thus the screw access whole would be directly at the incisal edge. Applying the angulated screw channel of the LTS-BASE® it may be shifted to oral.
The LTS-BASE® enables screwed solutions in positions where so far no screwing had been possible.
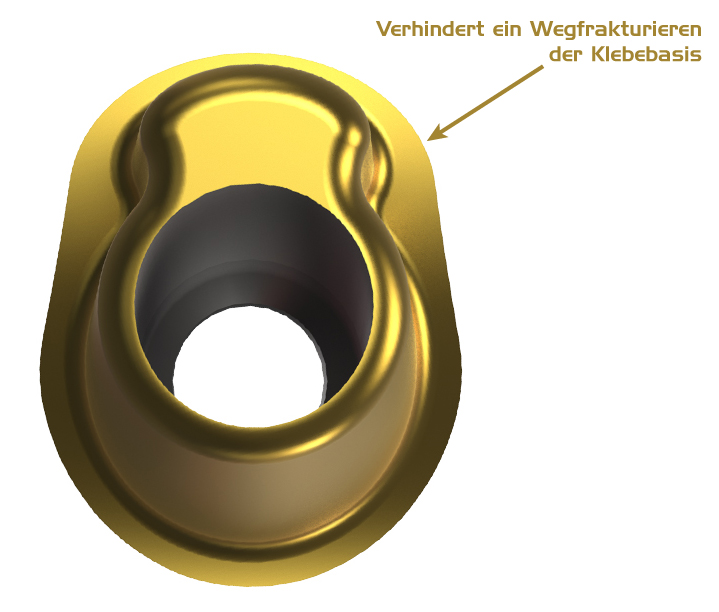
The Backpacker
The Backpaker’s Omega-shape offers a larger adhesive surface and stability
The Backpacker was developed to be able to offer both an enlarged adhesive surface and a higher stability. Abuntments 4 Life has the first angulated adhesive basis giving sufficient space to almost all situations at an angle of 11°. When shortening vestibularly, this may happen due to anatomic circumstances, you may gain a lot of space through the inverse inbus screw design in the area of this level. However, the stability of the Backpacker is not influenced by this as long as the angle chamfer does not exceed 38°.
When cutting the titanium adhesive base buccally (Cutt-off) only little adhesive surface remains for the adhesive body to prevent a fracture towards oral. The groove-shoulder-attachment of the Backpacker prevents a breaking of towards oral.
basal smooth vs. rough
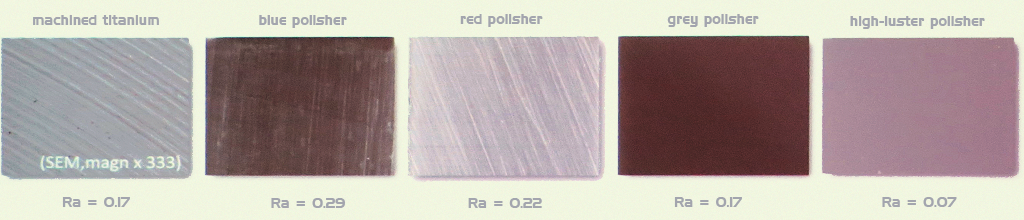
Rough is better than smooth!
Contrary to popular opinion, that the basal surface of the abutment has to be highly polished, several studies show that a rough surface with a microstructure is less risky for a peri-implantitis.
Abutments4life offers test specimen in different sizes, so grunding the ceramic body is not longer required. Because of the structured glue surface, sandblasting is also not longer required.
Literature
How to establish a suitable surface for zirkonia implant abutments under laboratory conditions.
Happe A, Röling N, Beuer F, Schäfer A, Nickenig H-J, Rothamel D:
Clinical Oral implants Research Vol 23 Suppl.7Oct 2012:44-45
More literature
- Smooth surfaces favour apical migration of junctional epithelium and do not favour cell adhesion.
Lindhe 1982, Brunette 1992, Guy 1993, Hormina & Könönen 1994, Cochran 1994, Meyle 1991
- Length of junct. epithel. was higher on smooth surfaces (2.9mm) than for rough surfaces (1.4-1.6mm), with an inverse relationship for the length oft he connective tissue in humans.
Glauser et al. 2005
- Clinically ultrapolished zirconia-abutments showed a slightly higher increase in probing depth and more bleeding on probing compared to machined titanium in humans.
Bollen 1996
- Smoothening of an intra-oral surface under a certain Ra-value (threshold Ra) of around 0.2 µm causes no further reduction of supra- and subgingival load of plaque.
Quirynen 1993, 1995, Bollen 1996
Structured adhesive surface
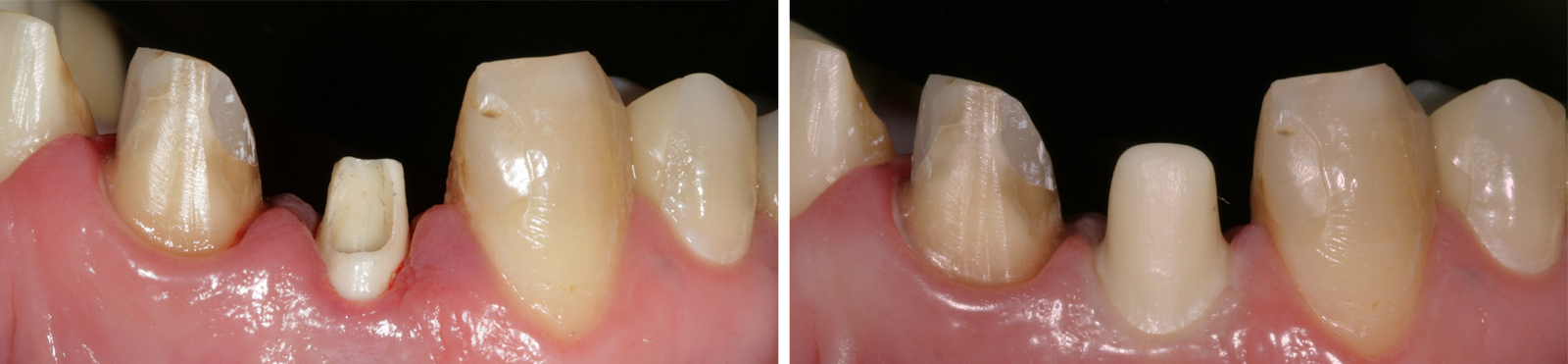
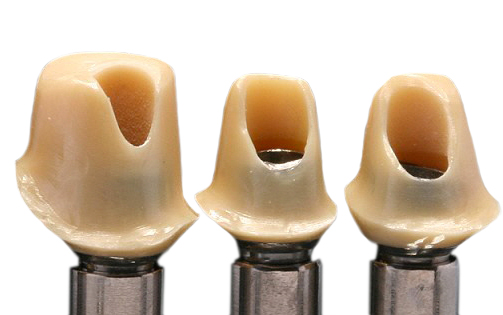
A structured (retentive) adhesive surface makes shot blasting unnecessary.
Conventional adhesive basis have to be sand blasted before bonding. This step costs both time and money. LTS-BASE®, however, have a surface especially adjusted to the grain size of the abuntment adhesives. This makes sand blasting redundant.
Esthetics
Occlusal support
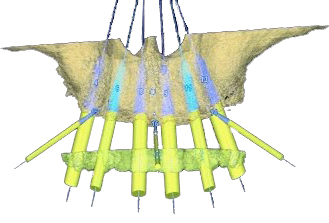
Compatibility to all common implant systems
Compatibility to all common implant systems
Abutments 4 Life offer numerous LTS-BASE® Abutment lines being compatible to all common implant systems.
We from Abutments4life
® would like to place all information about the application of the angulated titanium implant base here. Our aim is to facilitate the best possible esthetics and long-term stability at significantly reduced costs.
Welcome to Abutment solution with LTS-BASE
®.
Development of Abutments
All hitherto full-titanium abutments were and are still used successfully when fixing a crown onto an implant. They are straight and available with different angulations and in most cases they consist of titanium grade 5. But they are increasingly being replaced by hybrid abutments having a titanium base and a ceramic body.
Previous adhesive bases for hybrid abutments were only available in straight form, i.e. having the screw channel in the prolongation of the implant axis. The new LTS-BASE® offers, for the first time, an adhesive basis for hybrid abutments having an angulated screw channel.
Angulated abutments
The anatomy of the bone determines the direction of the axis for the implant, with the screw head restricting the maximum possible angulation.
In transversal and sagittal direction an adverse implant position may occur.
CAD vs. Clinics
There is very often a big difference between CAD design and the clinical situation.
This problem may be solved in various ways with titanium abutments:
A) The preparation margin is extremely far and unpredictably placed underneath the gingiva. But there is a big danger of cement leftovers remaining there after cementing.
B) The wrongly placed preparation margin has again to be moulded to adapt the abutment in the laboratory.
This procedure takes more time and is more expensive. Titanium abutments cannot be grounded intra-orally because of the danger of some tattooings.
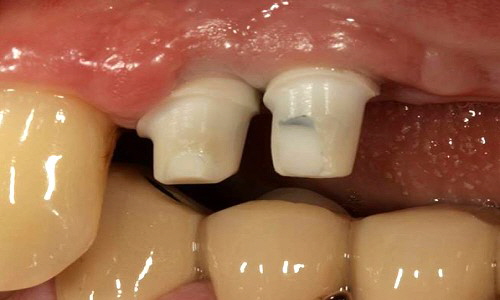
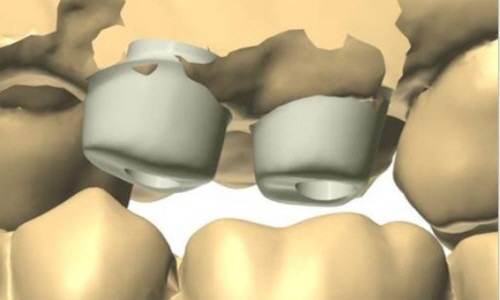
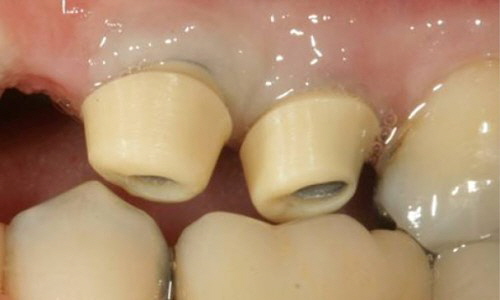
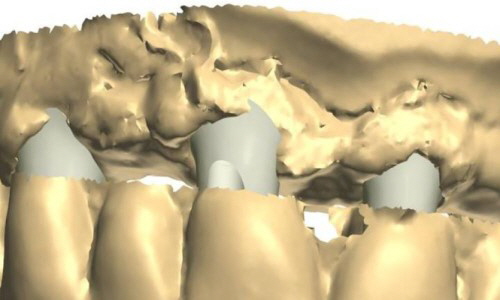
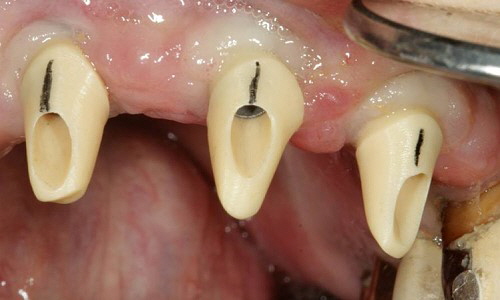 Being screwed vs. being cemented Being screwed vs. being cemented
If an angulation of the crown will be necessary, clinical situations may receive a prosthetic restoration when using the angulated screw access channel of the LTS-BASE®.
According to clinical studies, this holds true in more than 80 per cent of the cases in the aesthetic visual range.
Thus the screw access whole would be directly at the incisal edge. Applying the angulated screw channel of the LTS-BASE® it may be shifted to oral.
The LTS-BASE® enables screwed solutions in positions where so far no screwing had been possible.
The Backpacker
The Backpaker’s Omega-shape offers a larger adhesive surface and stability
The Backpacker was developed to be able to offer both an enlarged adhesive surface and a higher stability. Abuntments 4 Life has the first angulated adhesive basis giving sufficient space to almost all situations at an angle of 11°. When shortening vestibularly, this may happen due to anatomic circumstances, you may gain a lot of space through the inverse inbus screw design in the area of this level. However, the stability of the Backpacker is not influenced by this as long as the angle chamfer does not exceed 38°.
When cutting the titanium adhesive base buccally (Cutt-off) only little adhesive surface remains for the adhesive body to prevent a fracture towards oral. The groove-shoulder-attachment of the Backpacker prevents a breaking of towards oral.
basal smooth vs. rough
Rough is better than smooth!
Contrary to popular opinion, that the basal surface of the abutment has to be highly polished, several studies show that a rough surface with a microstructure is less risky for a peri-implantitis.
Abutments4life offers test specimen in different sizes, so grunding the ceramic body is not longer required. Because of the structured glue surface, sandblasting is also not longer required.
Literature
How to establish a suitable surface for zirkonia implant abutments under laboratory conditions.
Happe A, Röling N, Beuer F, Schäfer A, Nickenig H-J, Rothamel D:
Clinical Oral implants Research Vol 23 Suppl.7Oct 2012:44-45
More literature
- Smooth surfaces favour apical migration of junctional epithelium and do not favour cell adhesion.
Lindhe 1982, Brunette 1992, Guy 1993, Hormina & Könönen 1994, Cochran 1994, Meyle 1991
- Length of junct. epithel. was higher on smooth surfaces (2.9mm) than for rough surfaces (1.4-1.6mm), with an inverse relationship for the length oft he connective tissue in humans.
Glauser et al. 2005
- Clinically ultrapolished zirconia-abutments showed a slightly higher increase in probing depth and more bleeding on probing compared to machined titanium in humans.
Bollen 1996
- Smoothening of an intra-oral surface under a certain Ra-value (threshold Ra) of around 0.2 µm causes no further reduction of supra- and subgingival load of plaque.
Quirynen 1993, 1995, Bollen 1996
Structured adhesive surface
A structured (retentive) adhesive surface makes shot blasting unnecessary.
Conventional adhesive basis have to be sand blasted before bonding. This step costs both time and money. LTS-BASE®, however, have a surface especially adjusted to the grain size of the abuntment adhesives. This makes sand blasting redundant.
Esthetics
Occlusal support
Compatibility to all common implant systems
Compatibility to all common implant systems
Abutments 4 Life offer numerous LTS-BASE® Abutment lines being compatible to all common implant systems.
|